Colossal magnetoresistance materials
Thin films of so called “colossal magnetoresistance” (CMR) materials like La1-xSrxMnO3 or La1-xCaxMnO3 can be successfully grown using pulsed laser deposition or magnetron sputtering techniques. In the past, the following phenomena have been investigated by our group in close collaboration with other laboratories:
 1. The propagation of surface acoustic waves of a frequency around 100 MHz, generated by interdigital transducers in La0.67Ca0.33MnO3 films deposited on a piezoelectric lithium niobate substrates, leading to discovery of the anomalous electro-acoustic effect [1].
1. The propagation of surface acoustic waves of a frequency around 100 MHz, generated by interdigital transducers in La0.67Ca0.33MnO3 films deposited on a piezoelectric lithium niobate substrates, leading to discovery of the anomalous electro-acoustic effect [1].
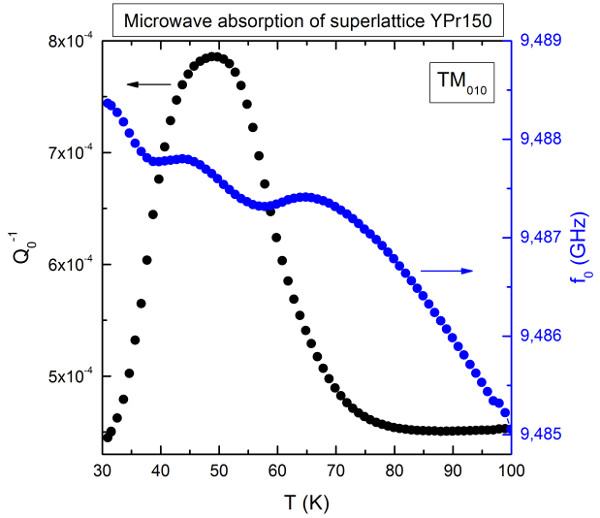
2. The lateral current flow in Re1−xBxMnO3/YBa2Cu3O7-x superlattices, where Re is La or Pr and B is Sr or Ca, which can be modelled as stacks of S/F/S Josephson tunnel junctions. These measurements were done by microwave absorption in the frequency range between 9 and 20 GHz [2].
Presently, the expected long-range proximity effect in nanobridges made out of the high-temperature superconductor YBa2Cu3O7-x deposited on top of La1-xSrxMnO3 or La1-xCaxMnO3 films is under investigation. These nanostructures are being patterned using focused ion beam (FIB) etching (this work is still in progress).
[1] Y. Ilisavskii, A.Goltsev, K. Dyakonov, V.P. Popov, E.Yakhind, V. Dyakonov, P. Gierłowski, A. Klimov, S. J. Lewandowski, H. Szymczak, "Anomalous Acoustoelectric Effect in La0.67Ca0.33MnO3 Films”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 87, 146602-1, (2001).
[2] P. Gierłowski, K. Werner-Malento, P. Przysłupski, C. J. van der Beek, "Microwave absorption in YBa2Cu3O7-δ -manganite superlattices”, Appl. Phys. Lett., 95, 172511 (2009).